Tax Series: Strategies for Private Corporations

Last summer, Finance Minister Morneau announced a number of tax reforms for Small Business Owners, including the changes to income sprinkling, minimizing the incentives to keep passive investments and reducing the transfer of corporate surpluses to capital gains.
This year’s Federal Budget focused on tax tightening measures for business owner:
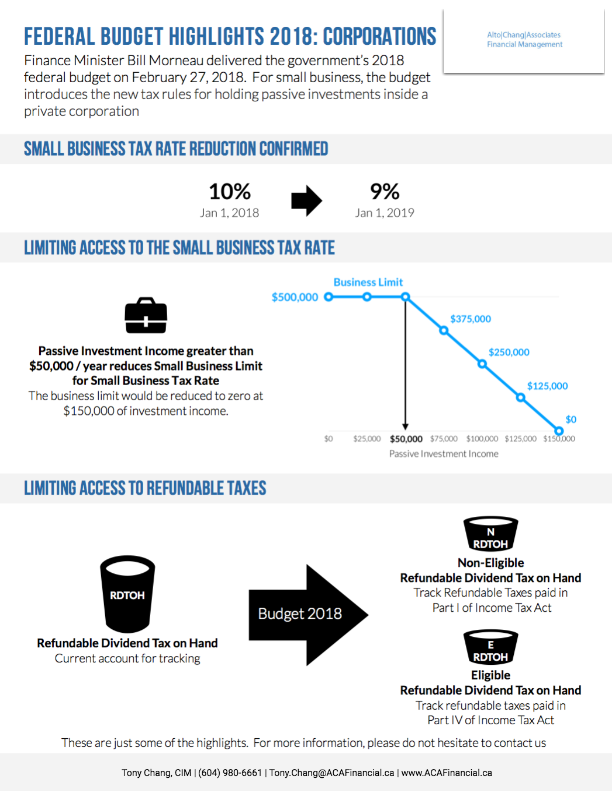
● Small Business Tax Rate Reduction from 10% to 9%.
● Passive Investment Income held within the corp (Reduction begins at $50,000)
● Tax on Split Income
Since these changes will be effective January 1, 2019, a discussion and plan should be prioritized now, since 2018 will be the “prior year” of 2019. Life insurance is a great solution to help business owners address these problems.
Reduced Small Business Tax Rate
● Key Change: Effective January 1, 2019, the small business tax rate will be reduced from 10% to 9%
● Problem: Lower corporate tax rates result in more capital trapped inside the corporation.
● Possible Solution: Life Insurance Proceeds credit the capital dividend account on death allowing for tax-efficient distribution of funds from the corporation to the estate.
Limited Access to Small Business Tax Rate
● Key Change: Passive investment income greater than $50,000/year reduces the small business tax rate limit for small business tax rate. The business limit is reduced to zero at $150,000 of investment income.
● Problem: For companies with passive income over $50,000, the small business limit will be reduced and thus, increase the total amount of tax you have to pay.
● Possible Solution: Exempt life insurance does not produce passive investment income unless there is a disposition. Put a portion of corporations passive investments into a life insurance policy and reduce passive investment income and limit the erosion of the small business limit. Concepts such as Corporate Estate bond, Corporate Insured Retirement Program, Corporate held Critical Illness with Return of Premium
Tax on Split Income
● Key Change: Tax on split income (TOSI) rules extended to cover adult children in certain cases. Different rules depending on age of adult children
● Problem: For adult children receiving income and don’t pass the TOSI rules, income is taxed at the highest personal marginal tax rate on the first dollar. More trapped funds inside the corporation due to fewer tax-effective strategies.
● Possible Solution: Put a portion of corporation’s trapped surplus into a corporate owned life insurance policy which results in tax-efficient distribution of funds from the corporation to the estate.