How to apply for EI benefits for COVID-19 quarantines and other support programs
What are EI benefits for those quarantined with COVID-19?
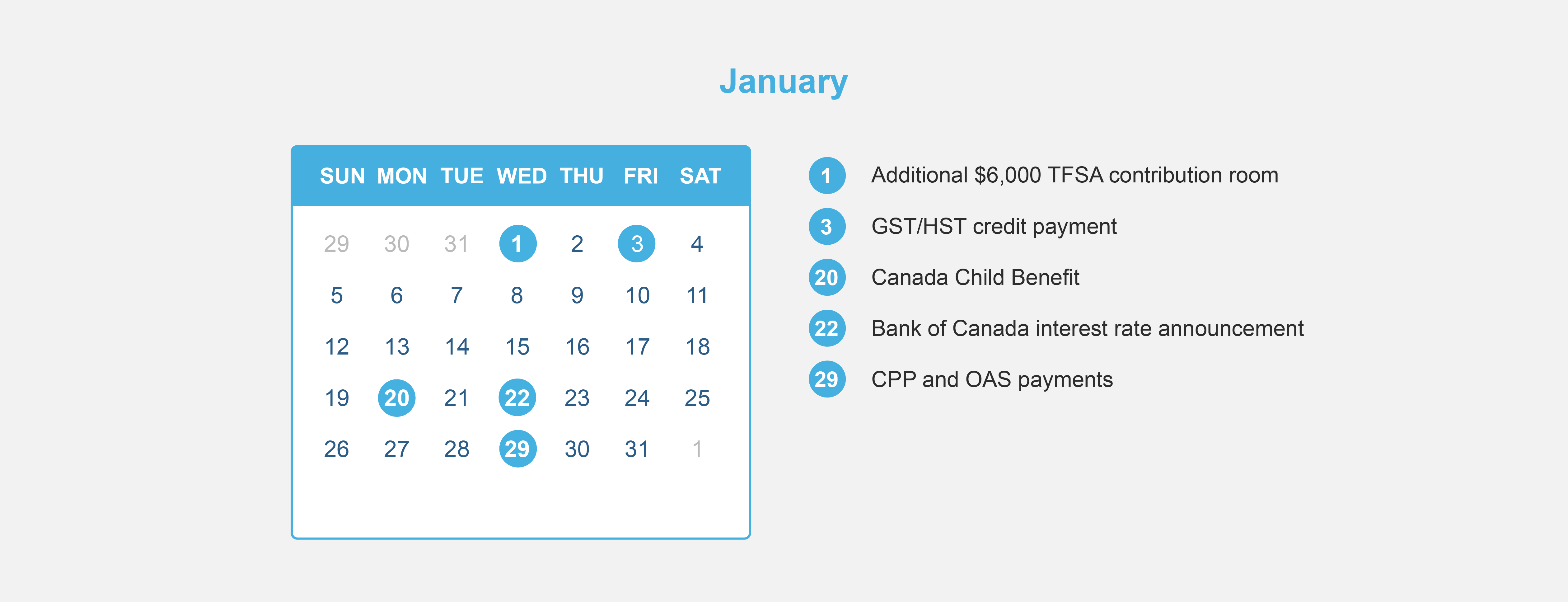
Employment Insurance (EI) sickness benefits provide up to 15 weeks of income replacement and is available to eligible claimants who are unable to work because of illness, injury or quarantine, to allow them time to restore their health and return to work. Canadians quarantined can apply for Employment Insurance (EI) sickness benefits.
Is there a waiting period?
For quarantine because of COVID-19, the one week waiting period is waived. Contact the new dedicated toll-free phone number if you are in quarantine and seeking to waive the one-week EI sickness benefits waiting period so you can be paid for the first week of your claim:
-
Telephone: 1-833-381-2725 (toll-free)
-
Teletypewriter (TTY): 1-800-529-3742
What benefits does EI offer?
Employment Insurance (EI) sickness benefits can provide you with up to 15 weeks of financial assistance if you cannot work for medical reasons. You could receive 55% of your earnings up to a maximum of $573 a week.
Who qualifies for EI sick-leave benefits?
Employed Canadians who pay EI premiums and self-employed people registered for access to EI may be eligible for sickness benefits.
There are a number of factors that determine eligibility. You need to demonstrate that:
-
you’re unable to work for medical reasons
-
your regular weekly earnings from work have decreased by more than 40% for at least one week
-
you accumulated 600 insured hours* of work in the 52 weeks before the start of your claim or since the start of your last claim, whichever is shorter
*As an example, 600 hours are equivalent to 20 weeks of work at 30 hours a week.
While you’re receiving sickness benefits, you must remain available for work if it weren’t for your medical condition.
If you are self-employed and pay into EI, you have to wait at least 12 months from the date of your confirmed registration before you are eligible for sickness benefits. You must also meet all of the following conditions:
-
The amount of time you spend on your business has decreased by more than 40% for at least one week because of your medical condition
-
You earned a minimum amount of self-employed earnings during the calendar year before the year you apply for benefits. To receive benefits for 2020, you need to have earned at least $7,279 in 2019
What if I don’t qualify for EI?
In April, the government will be introducing the Emergency Care Benefit providing up to $900 bi-weekly, for up to 15 weeks. This flat-payment Benefit would be administered through the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) and provide income support to:
-
Workers, including the self-employed, who are quarantined or sick with COVID-19 but do not qualify for EI sickness benefits.
-
Workers, including the self-employed, who are taking care of a family member who is sick with COVID-19, such as an elderly parent, but do not qualify for EI sickness benefits.
-
Parents with children who require care or supervision due to school or daycare closures, and are unable to earn employment income, irrespective of whether they qualify for EI or not.
Application for the Benefit will be available in April 2020, and require Canadians to attest that they meet the eligibility requirements. They will need to re-attest every two weeks to reconfirm their eligibility. Canadians will select one of three channels to apply for the Benefit:
-
by accessing it on their CRA MyAccount secure portal;
-
by accessing it from their secure My Service Canada Account; or
-
by calling a toll free number equipped with an automated application process.
Do you need a Doctor’s note?
According to the Government of Canada’s website, people claiming EI sickness benefits due to quarantine will not have to provide a medical certificate.
How do I get started with the application for EI to see if I qualify?
The application for Employment Insurance can be found here: